40 human skull diagram with labels
Trunk Region (Torso) < Regional Anatomy << Human Anatomy <<< Body ... Trunk (Torso) In our body, the Trunk Region (Torso), an anatomical term for the central part of the body, is a combination of both the thoracic region (chest), including the mammary region (breasts), and the abdomen region (belly region) including the naval (umbilicus region), coxal region, and pubic region. In our body, the Trunk Region (Torso) as an anatomical term for the central part of ... Structure of the Brain and Their Functions | New Health Advisor It takes up 60% of brain matter. Numbers- The brain is made up of 75% water. It has 60% fat thus making it the fattest organ in the body. It has at least some 100,000 miles of blood vessels in the brain. The brain generates between 10 -23 watts of energy whilst you are awake and this is sufficient to light up a bulb.
Ribs: Anatomy, ligaments and clinical notes | Kenhub The body ends with a cup for the costal cartilage, which allows the rib to articulate with the sternum. Atypical ribs The first, second and tenth to twelfth ribs are known as atypical and as such will be considered individually. First rib The first rib is the widest, shortest and has the sharpest curve of all the ribs.
Human skull diagram with labels
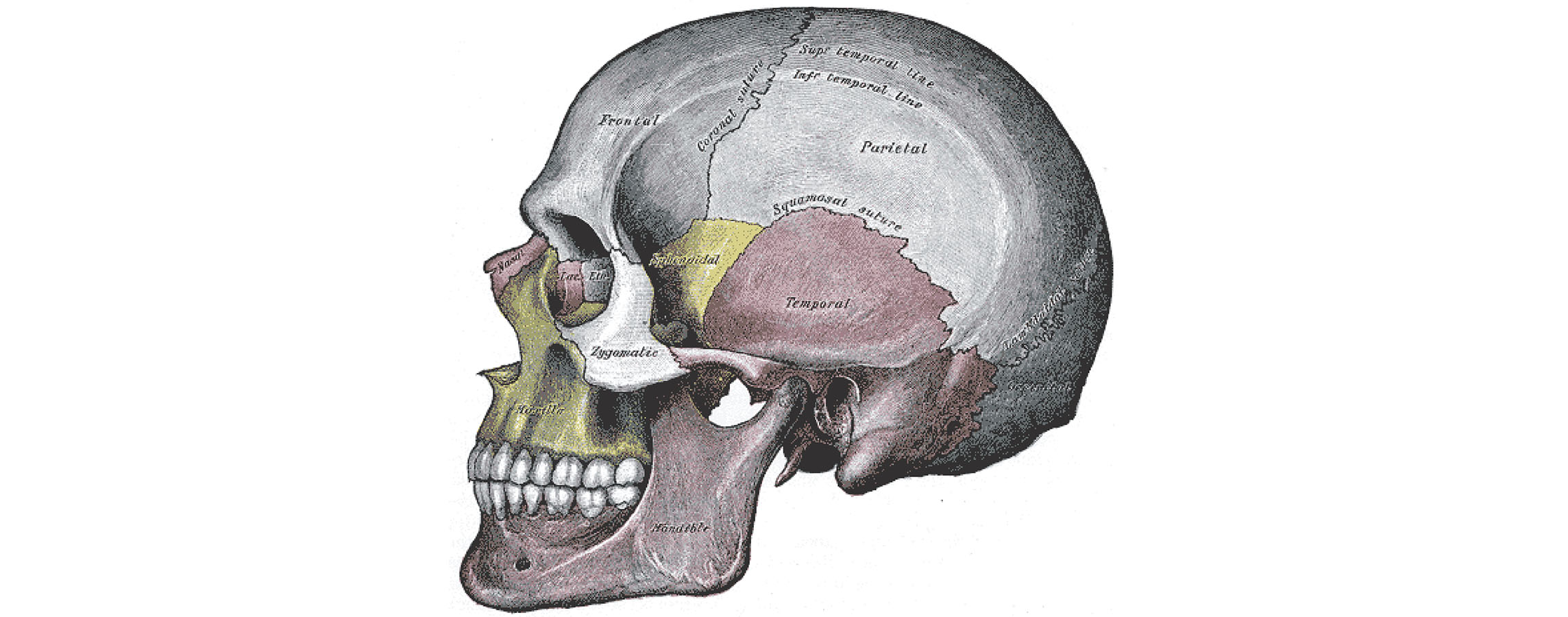
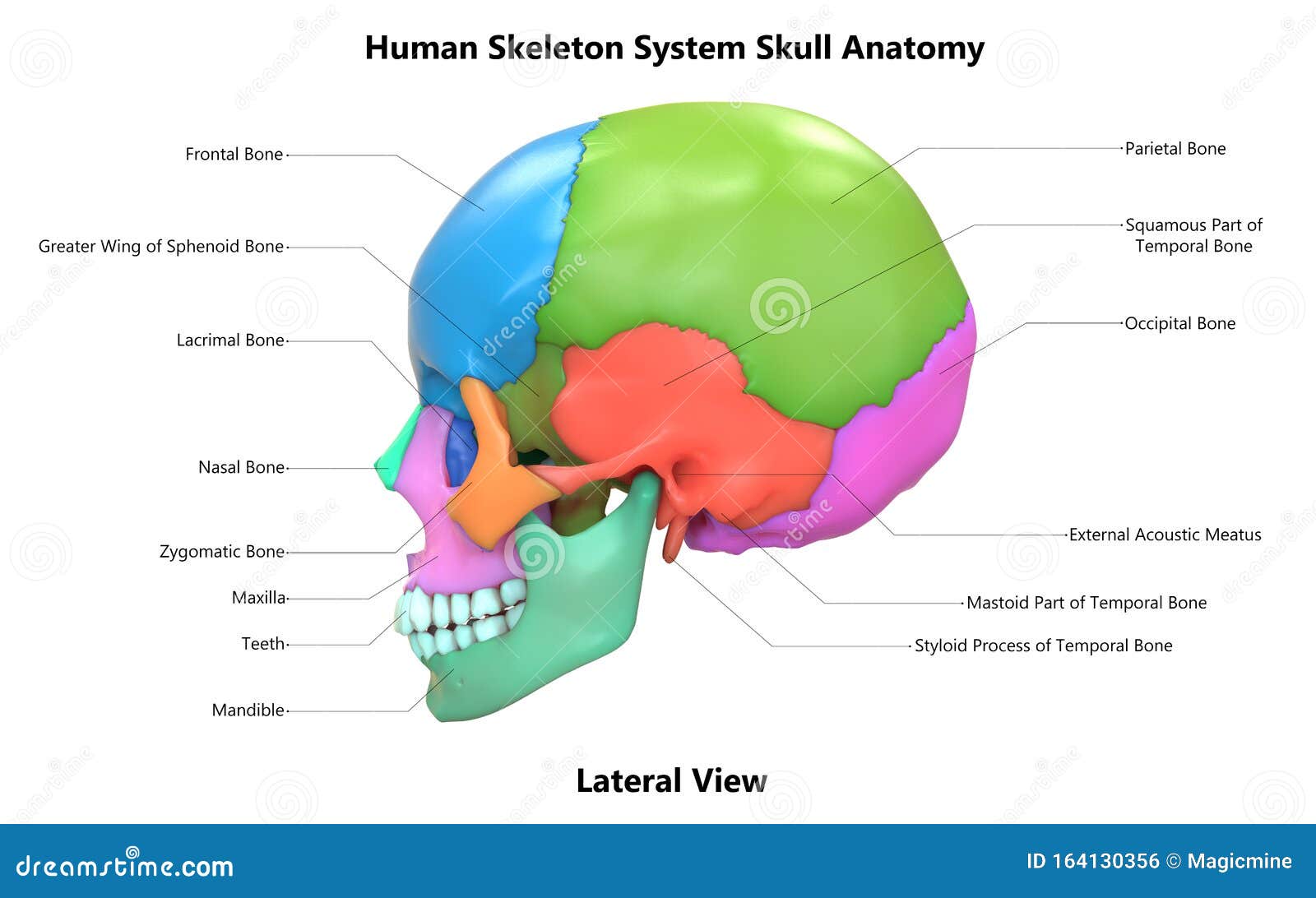
Sphenoid Bone | GetBodySmart The temporal bones are facial bones which located at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. Parietal Bone Anatomy The parietal bone is a large, thin, four-sided cranial bone that makes up much of the top and sides of the cranium. Learn about the different markings of the parietal bone. Femur: anatomy and labeled diagram | GetBodySmart The femur ( os femoris) extends from the hip to the knee and is the longest and strongest bone in the body. Forming the midportion of the femur is a long cylindrical shaft, which arches or curves anteriorly. At its proximal end, the spherical head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum ( hip socket) of the os coxa ( hip bone) to form the ... Primate - Wikipedia The primate skull has a large, domed cranium, which is particularly prominent in anthropoids. The cranium protects the large brain, a distinguishing characteristic of this group. The endocranial volume (the volume within the skull) is three times greater in humans than in the greatest nonhuman primate, reflecting a larger brain size.
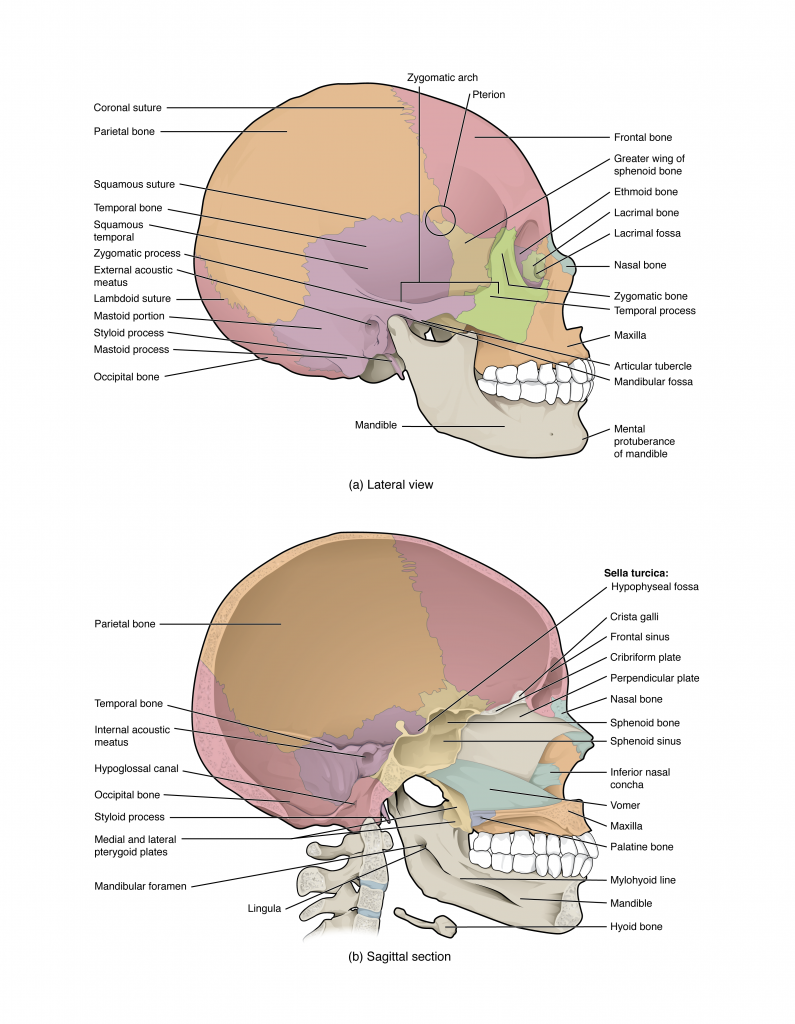
Human skull diagram with labels. Anatomy & Physiology: BIO 161 / 162 - Community College of Allegheny County Lab 4: Introduction to the Skeleton and Bone Histology ; Lab 5: The Axial Skeleton ; Lab 6: The Appendicular Skeleton ; Lab 7: Joint Structure / Articulations ; Lab 8: Introduction to Muscle Tissue ; Lab 9: Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System ; Lab 10: Introduction to the Nervous System ; Lab 11: Brain and Cranial Nerves Prostate: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment - Verywell Health The prostate is an important gland located between the penis and bladder. It sits just to the front of the rectum. The urethra, which carries urine from the bladder out of the body, runs through the center of this walnut-sized organ. The gland's primary function is to secrete fluid that nourishes sperm and keeps it safe. 1. Scapula Bone | GetBodySmart Slide for label 1 2 Markings of the Scapula Bone: It has three borders (superior, lateral, medial), three angles (superior, lateral, medial) and two surfaces (costal, dorsal). A prominent ridge or spine divides the dorsal surface into two, unequal parts called the supraspinous fossa and infraspinous fossa. Diaphragm: Location, anatomy, innervation and function | Kenhub The diaphragm is a musculotendinous structure with a peripheral attachment to a number of bony structures. It is attached anteriorly to the xiphoid process and costal margin, laterally to the 11th and 12th ribs, and posteriorly to the lumbar vertebrae. The posterior attachment to the vertebrae is by tendinous bands called Diaphragm Diaphragma 1/3
Anatomy of the Integumentary System - Verywell Health Frequently Asked Questions. The integumentary system is the body's outermost layer. Composed of skin, hair, nails, glands, and nerves, its main job is to protect your insides from elements in your environment, like pollution and bacteria. It also helps retain bodily fluids, eliminate waste products, and regulate body temperature. Diagram of Human Heart and Blood Circulation in It Exterior of the Human Heart A heart diagram labeled will provide plenty of information about the structure of your heart, including the wall of your heart. The wall of the heart has three different layers, such as the Myocardium, the Epicardium, and the Endocardium. Here's more about these three layers. Epicardium Organs of Skeletal System and Their Functions - New Health Advisor It contains the following from top to bottom respectively: Skull- it includes the cranium, face and auditory ossicles. Hyoid - bone of neck for muscles attachment of chin and larynx. Vertebral column - consist of all spinal vertebrae. Thoracic cage - it contains ribs and sternum. Appendicular Skeleton Megalodon - Wikipedia The genus Carcharocles currently contains four species: C. auriculatus, C. angustidens, C. chubutensis, and C. megalodon.: 30-31 The evolution of this lineage is characterized by the increase of serrations, the widening of the crown, the development of a more triangular shape, and the disappearance of the lateral cusps.: 28-31 The evolution in tooth morphology reflects a shift in predation ...
How to Work Safely with - Hazardous Products using the "Skull and ... The symbol within the pictogram is a human skull with two crossed bones behind it. The symbol indicates that hazardous products with this pictogram can cause death or poisoning. Hazardous products with this pictogram can be safely worked with if proper storage and handling practices are followed. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) - Genome.gov Definition. …. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell. WHMIS 2015 - Pictograms : OSH Answers - Canadian Centre for ... The skull and crossbones pictogram is used for the following classes and categories: Acute toxicity - Oral (Category 1, 2 and 3) Dermal (Category 1, 2 and 3) Inhalation (Category 1, 2 and 3) The health hazard pictogram is used for the following classes and categories: Radius and Ulna Bones Anatomy | GetBodySmart The radius and ulna are the bones of the forearm. The forearm is the region of the upper limb that extends from the elbow to the wrist. The radius bone ( os radius) supports the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm and the ulna bone ( os ulna) supports the medial (little finger) side. 1 2 3
Elbow and forearm: Forearm muscles and bones anatomy | Kenhub Diagram showing the bones and ligaments of the forearm The forearm consists of two long bones; the radius and the ulna. The ulna is located medially and is both longer and larger than the radius, which runs parallel to it laterally. These two bones are held together by the intervening interosseous membrane.
Spinal Cord Cross Section | New Health Advisor The tracks that move upward are responsible for signals to the brain and the descending tracts send the signals from the brain to neurons throughout the body. 2. Gray Matter In the center of the gray matter you will find the cerebrospinal fluid. The specific horns of the gray matter are responsible for different things.
Thoracic cage: Anatomy and clinical notes | Kenhub The thoracic cage (rib cage) is the skeleton of the thoracic wall. Structural components. 12 thoracic vertebrae with their intervertebral discs, 12 pairs of ribs and their associated costal cartilages and sternum. Intercostal spaces. Named according to the rib forming the superior border and contain intercostal muscles, vessels, and nerves.
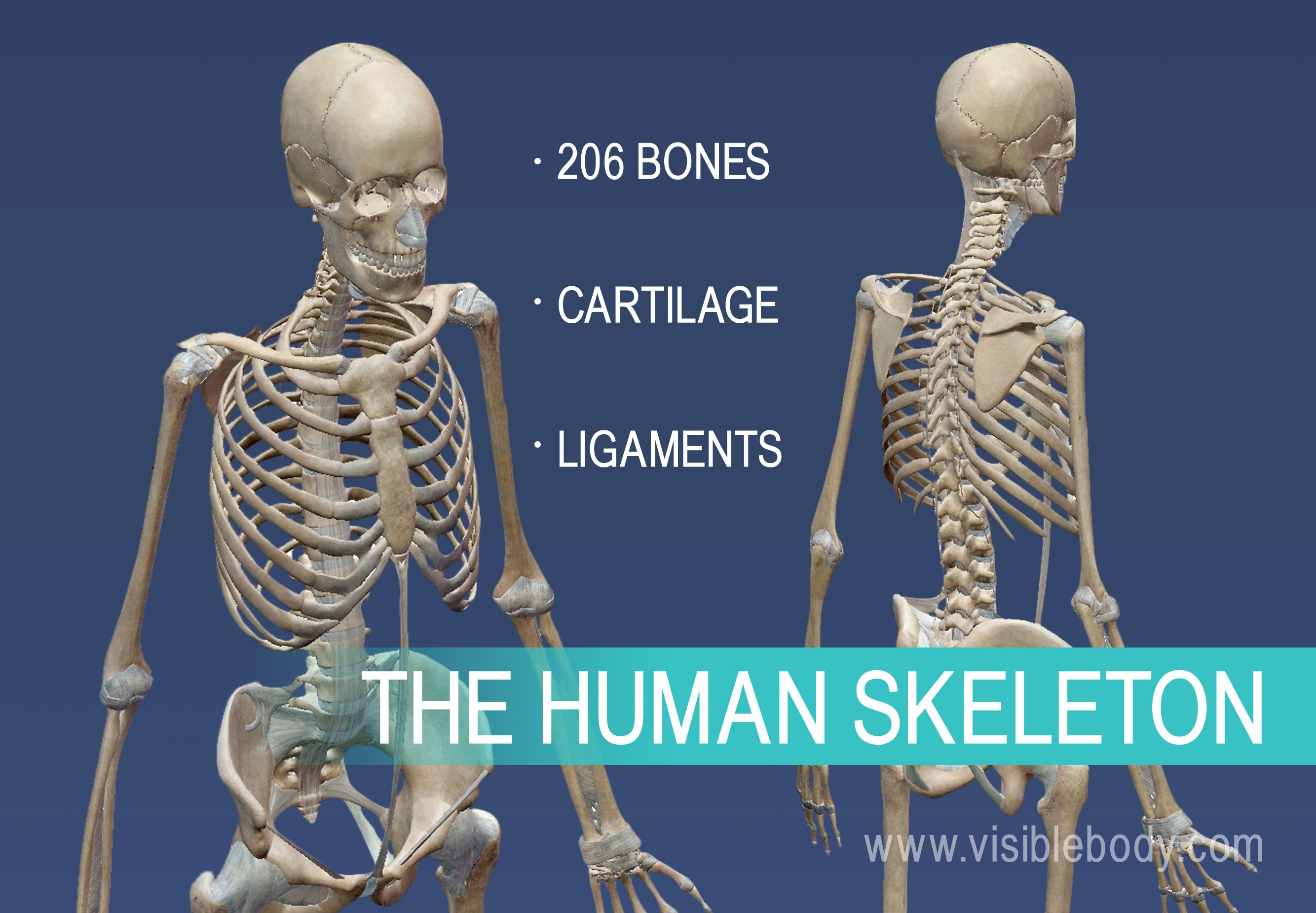
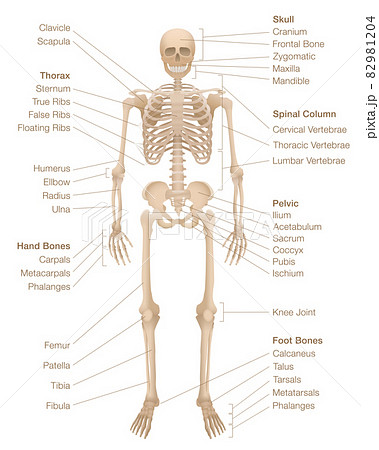
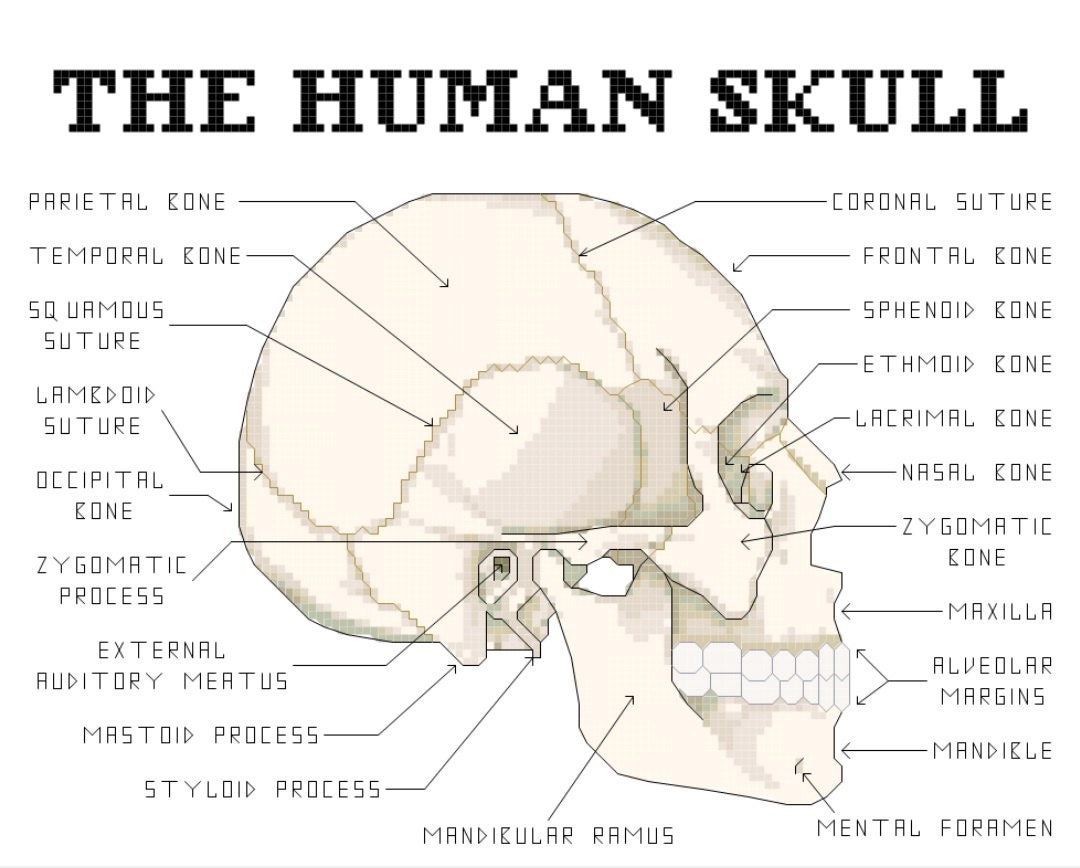
The Skeletal System Anatomy | Health Life Media Skeletal system Anatomy. The skeletal system is an adult body made up of 206 individual bones. These bones are arranged into two major divisions: the appendicular skeleton and the axial skeleton. The axial skeleton continues along the body's midline axis and consists of 80 bones in the following regions. Skull.
Antenatal Care Module: 6. Anatomy of the Female Pelvis and Fetal Skull ... You can locate the main skull bones in Figure 6.5. View larger image Figure 6.5 Bones of the fetal skull — side view facing left. The fetal skull bones are as follows: The frontal bone, which forms the forehead. In the fetus, the frontal bone is in two halves, which fuse (join) into a single bone after the age of eight years.
mouth | Definition, Anatomy, & Function | Britannica mouth, also called oral cavity or buccal cavity, in human anatomy, orifice through which food and air enter the body. The mouth opens to the outside at the lips and empties into the throat at the rear; its boundaries are defined by the lips, cheeks, hard and soft palates, and glottis. It is divided into two sections: the vestibule, the area between the cheeks and the teeth, and the oral cavity ...
17 Different Types of Bone Fractures | New Health Advisor 4. Transverse Fracture. This fracture is perpendicular to the axis of the bone. You get a transverse fracture when something applies serious force at a right angle to the bone. 5. Spiral Fracture. You have a spiral fracture when the fracture line twists around the bone.
Anatomy Project - Sheridan College Modify, alter or inappropriately use any content included in this resource Copy and post any digital representation of the 3D skeletal model in a public forum, such as, but not limited to, Facebook, Snapchat, Instagram, etc. Use any content in published scholarly works without express written permission of the creators of the work

Structure of the human skull with main parts colored and labeled. Lateral view. Medical vector illustration in flat style on white background
Positions and Functions of the Four Brain Lobes | MD-Health.com The brain is divided into four sections, known as lobes (as shown in the image). The frontal lobe, occipital lobe, parietal lobe, and temporal lobe have different locations and functions that support the responses and actions of the human body. Let's start by identifying where each lobe is positioned in the brain. Position of the Lobes
Skeleton | Skeletal System Overview | GetBodySmart The adult human skeleton is a framework of 206 bones and is anatomically divided into two parts, the axial skeleton, and the appendicular skeleton. Axial Skeleton: The axial skeleton is the core of the skeleton, it consists of the following 80 bones: Skull: 22 bones Hyoid: 1 bone Vertebrae: 32 bones Ribs: 24 bones Sternum: 1 bone 1 2 3 4 5 6
Nerve Supply Of The Jaws And Teeth - Dental Anatomy - Global Healthcare (1) The maxillary teeth. The maxillary nerve on each side passes forward in the floor of the orbit of the eye. It first gives off the posterior superior alveolar branch to the three maxillary molars. When in the floor, the maxillary nerve gives off a middle superior alveolar branch to the maxillary bicuspids and mesial root of the first molar.
Primate - Wikipedia The primate skull has a large, domed cranium, which is particularly prominent in anthropoids. The cranium protects the large brain, a distinguishing characteristic of this group. The endocranial volume (the volume within the skull) is three times greater in humans than in the greatest nonhuman primate, reflecting a larger brain size.
Femur: anatomy and labeled diagram | GetBodySmart The femur ( os femoris) extends from the hip to the knee and is the longest and strongest bone in the body. Forming the midportion of the femur is a long cylindrical shaft, which arches or curves anteriorly. At its proximal end, the spherical head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum ( hip socket) of the os coxa ( hip bone) to form the ...
Sphenoid Bone | GetBodySmart The temporal bones are facial bones which located at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. Parietal Bone Anatomy The parietal bone is a large, thin, four-sided cranial bone that makes up much of the top and sides of the cranium. Learn about the different markings of the parietal bone.
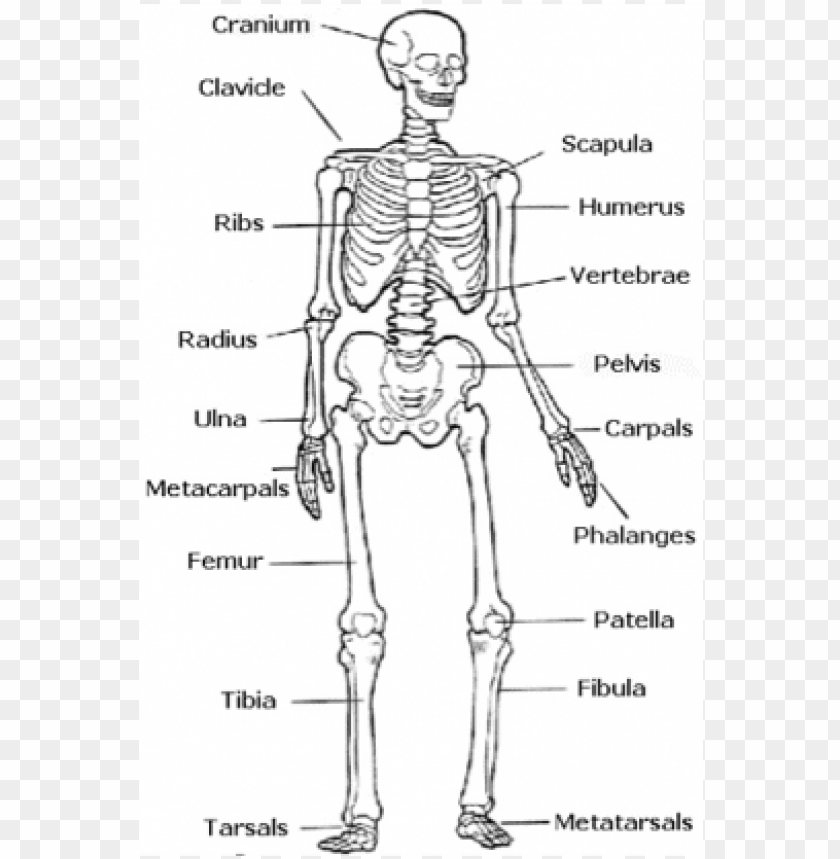






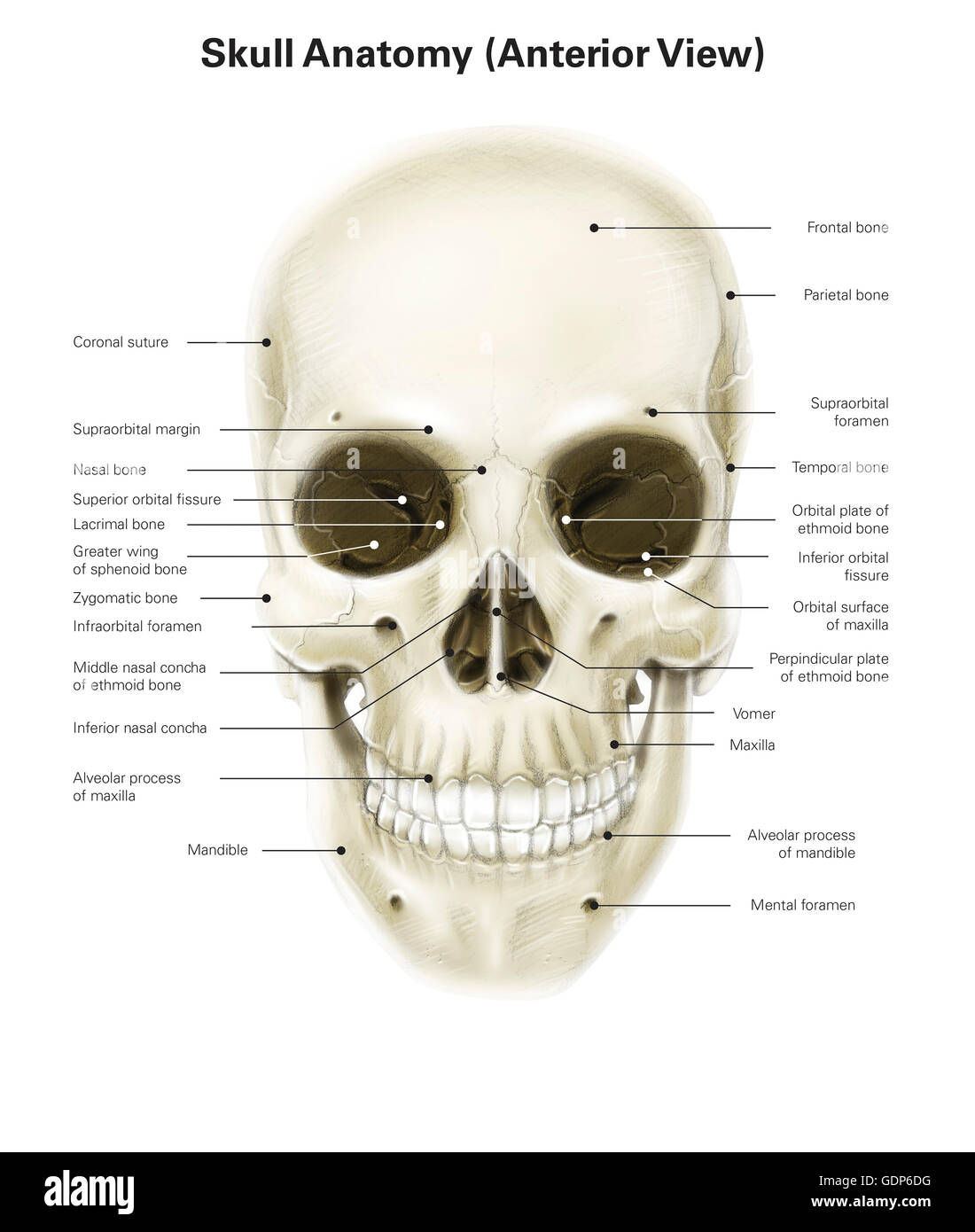
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11336/labaled_diagram_main_bones_of_skull.jpg)

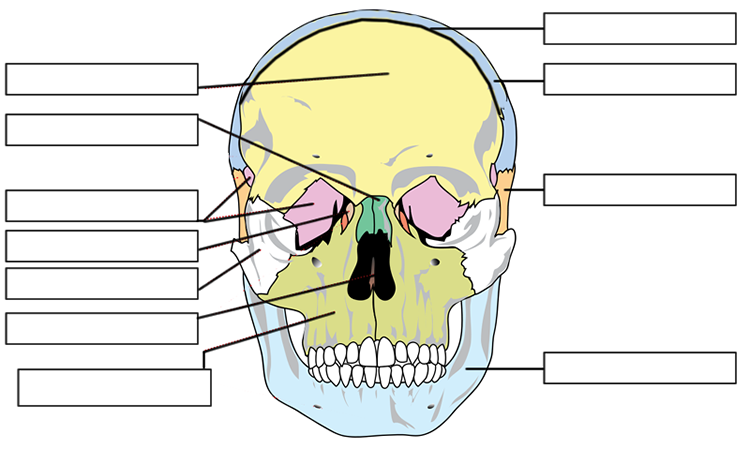
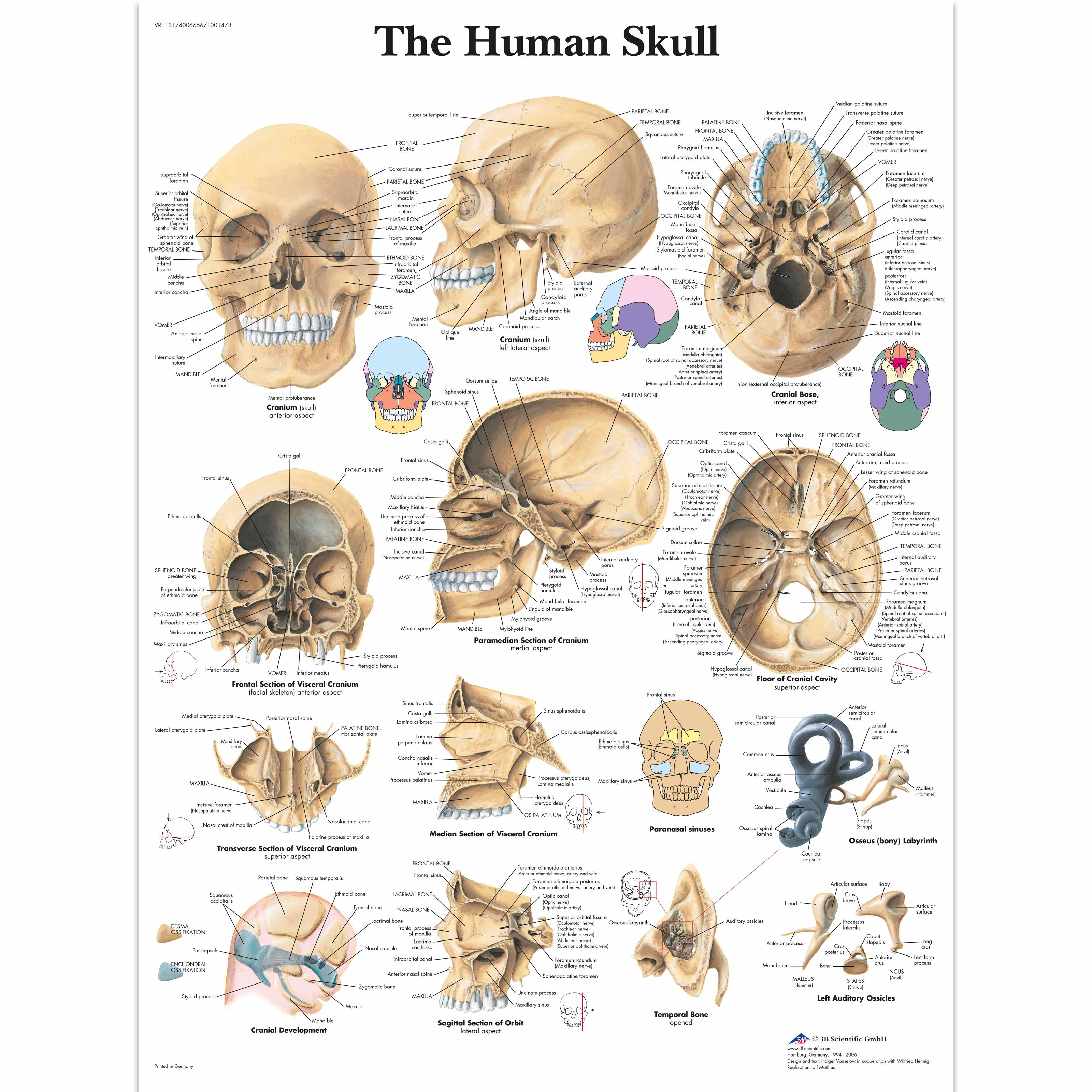




:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10684/skull-anterior-lateral-views_english.jpg)

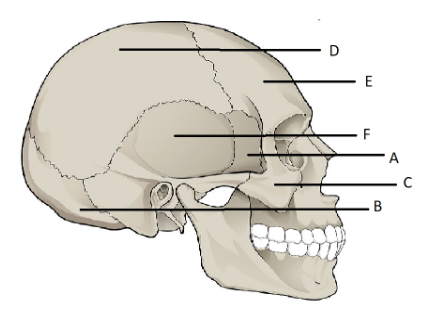







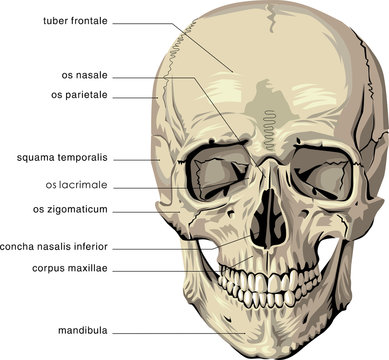


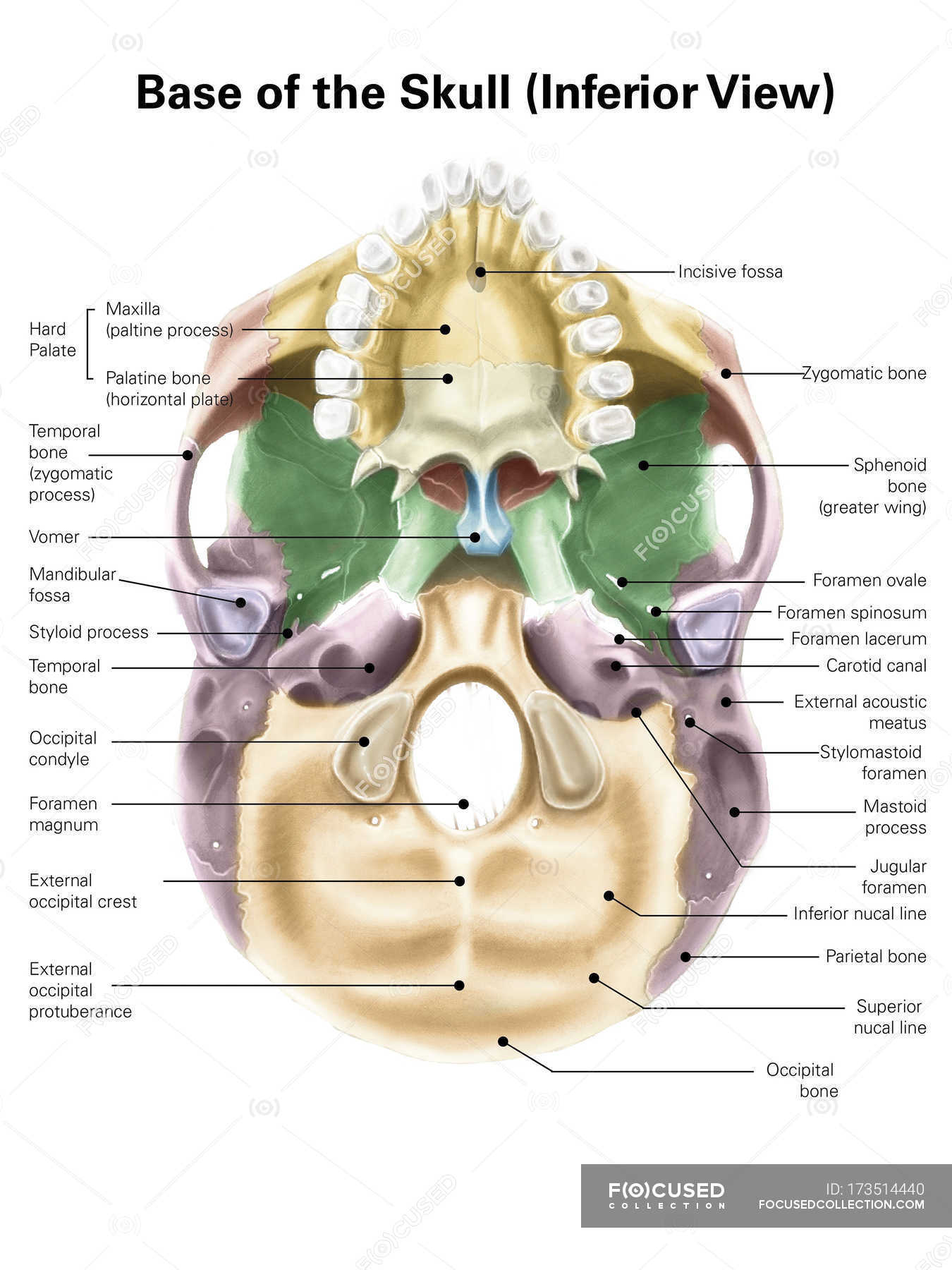
Post a Comment for "40 human skull diagram with labels"